What is a VPLS?
A VPLS (Virtual Private LAN Service) is a network protocol that allows users to connect many different ethernet-based local area networks together over long distances. VPLS uses MPLS data packets and the Internet in order to forward information from one or more computers in one network to one or more computers in another network and then expand that to include even further networks that are all connected via the VPLS. Businesses and government agencies that have branches in many different locations generally use VPLS systems. However VPLS systems can also be used for gaming and other purposes that require networks to send and receive data outside of each network’s physical operation range.
How VPLS Works
VPLS networks work in similar to both LAN and MPLS networks. In a VPLS system, data is arranged in packets and labeled according to what it is, where it came from, and where it is going. Each packet is then sent to the nearest computer within the network in alphabetical order. As each computer receives the data packets, it forwards them to the next computer in line until the data reaches the end of the network. While an MPLS network prevents the data from travelling any further, a VPLS network allows the last computer in the network to forward the data to the nearest network in the system. This expands the primary network’s physical operation range to both the primary and secondary networks’ physical 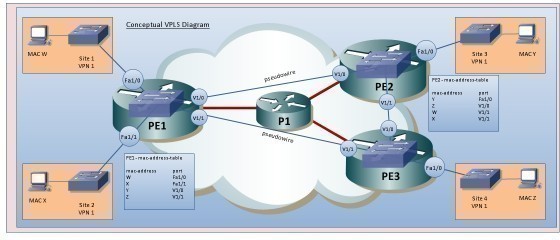 operation range.
operation range.
Applications
VPLS networks have many uses, but are generally connect a business or institution’s individual network together over long distances. This allows those institutions to efficiently archive and sort through all of the data being generated by their overall efforts, rather than being dependent on their individual branches to forward data to a central database and then requiring staff members to organize all of that data.
Advantages
VPLS networks have several critical advantages over other types. They connect many different computers over a much further distance than local area networks, wide area networks, and wireless networks. VPLS networks emulate physical connections even though they are only connected via the Internet and can be scaled to work with any network size.


Comments - No Responses to “What is a VPLS?”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.