Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems
Tire pressure monitoring systems (TPMS) are used to detect the air pressure of automobile tires and provide warnings to the operator when the pressure is low. They are electronic devices and are also referred to as tire pressure indication systems depending on the device’s manufacturer. Most variants of the system display a warning light to the vehicle operator, and some also display the real time pressure of each tire on the automobile.
What Are the Types of Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems?
There are two types of tire pressure monitoring systems: direct and indirect. The direct-sensor system uses a physical pressure system that is installed inside of each tire and can determine under-inflation in any of the four tires on the vehicle. These sensors are made to take the friction created through vehicle movement on the tires into account and are normally set during cold tire inflation temperatures. The direct-sensor uses either electromagnetic coupling or a radio-frequency (RF) transmission to send data from these sensors to the automobile’s electronic system. Battery-powered RF systems add another component to the automobile that can fail due to age or extreme temperature exposure. They also have a higher ownership cost than “battery-less” options for direct-sensor monitoring systems.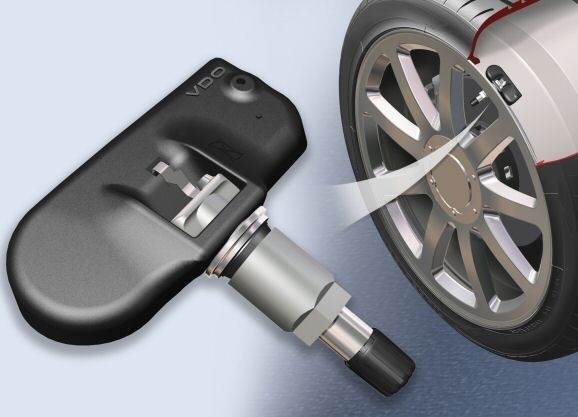
Indirect tire-pressure monitoring systems do not use physical sensors. Instead, they estimate the air pressure of the tires by taking note of the wheel rotation speed and other factors that can indicate an under-inflated tire. The indirect system’s latest models also use vibration analysis techniques to determine if tires are under-inflated. However, these newer sensors sometimes require suspension sensors, which increase the overall cost of the systems.
How Are Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems Setup?
Tire pressure monitoring systems have to be installed and tested when the automobile is manufactured. The sensors are attached to the wheel during the assembly process and then the wheels are installed on the vehicle. If an RF-based sensor is being used, the system’s unique identification and wheel positions are downloaded to the specific automobile’s computer. When vehicles are serviced, the repair shop may need to use this information in order to ensure that the car’s computer is updated with the proper information when changing or rotating tires. Hand held computers support current tire pressure monitoring systems, which are available to those doing their own repair work. This prevents automobile owners from having to depend on the vehicle’s manufacturer for tire maintenance.
Tire Pressure Monitoring System Performance
Tire pressure monitoring systems were initially developed in order to help reduce the number of annual road fatalities attributed to tire defects. A secondary reason was to help improve overall fuel economy through consumers driving their automobiles on properly inflated tires. Unfortunately, the first tire monitoring systems were not designed to accommodate increased heat build-up from tire friction and other environmental conditions, making them unpopular. Technological improvements have changed this in recent years. It is required that tire pressure monitoring systems are installed on all (2007 and up) vehicles sold in the United States. Systems installed in the U.S. are required by law to warn the driver when tire pressure is 25% below the recommended amount for the vehicle.


Comments - 3 Responses to “Tire Pressure Monitoring Systems”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.