Static Class Members
The members (data members and member functions) of a class may be qualified as static by preceding member declaration with the keyword static. There may be static data members and static member functions in a class.
Static Data Member
A static data member of a class is just like a global variable for its class. That is, this data member is globally available for all the objects of that class type. The static data members are usually maintained to store values common to the entire class. For instance, a class may have a static data member keeping track of its number of existing objects.
A static data member is different from ordinary data members of a class in various respects:
- There is only one copy of a static data member maintained for the entire class which is shared by all the objects of that class.
- It is visible only within the class; however, its lifetime (the time for which it remains in the memory) is the entire program.
Two things are needed for making a data member static:
- Declaration within the class definition
- Definition outside the class definition.
The declaration of a static data member within the class definition is similar to any other variable declaration except that it starts with the keyword static as shown below:
The definition, of above declared static member count, outside the class will be as follows:
A static data member must be defined outside the class definition as these are stored separately rather than as a part of an object.
Note: A static data member must be defined outside the class definition.
Since, they are associated with the class itself rather than with any class object, they are also known as class variables. Following figure shows how a static data member is shared by all the objects.
A static data member can be given an initial value at time of its definition as shown below:
The above definition initializes count with value 10.
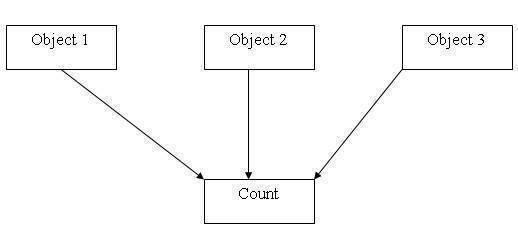
Fig : Sharing of a static data member
Static Member Function
A member function that accesses only the static members of a class may be declared as static. This can be done by putting keyword static before the function declaration in the class definition as shown below:
By just prefixing the keyword static before the function declaration in the class definition, you have declared the function as static.
A static member function is different from other member functions in various respects:
- A static member function can access only static members (functions or variables) of the same class.
- A static member function is invoked by using the class name instead of its objects as it is shown below:
That is, to call the static function show( ) of above defined class X, you will write
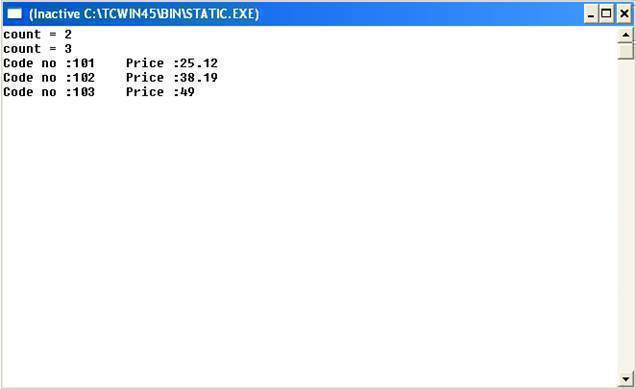
Example: Program to keep a count of created objects using static members.
Output:


Comments - No Responses to “Static Class Members”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.