Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh scattering refers to a phenomenon in which light is scattered by particles in the atmosphere that are much smaller than its wavelength. It can also apply to other forms of electromagnetic radiation as well as other media, but can be seen most directly in the sky. Rayleigh scattering is responsible for the sky’s many different colors, such as blue during the day, orange at sunset, and even the yellow hue of the Sun. Different wavelengths of light that are reflected off of small molecules, dust, and other particles in the air cause these different colors.
How Rayleigh Scattering Works
As light travels through the atmosphere, it comes in contact with many different types of debris that cause the light to reflect in various directions or scatter. As the light scatters, its wavelengths are spread out and the human eye observes them as various colors, depending on the reflection’s angle, type of material, and wavelength of light.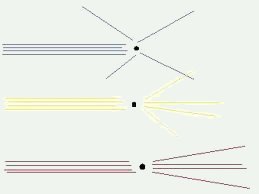
Applications
While Rayleigh scattering allows observers to witness a wide variety of beautiful colors in the sky, it can also be used for practical applications. For example, Rayleigh scattering is used in LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) to calculate the distance between two endpoints of a beam of light. Rayleigh scattering is also used in weather RADAR systems to detect storm formation before a storm causes damage.
Advantages
Rayleigh scattering is advantageous because it allows observers to view the many different wavelengths of light and other electromagnetic waves by shining light through a gas. Because of this, Rayleigh scattering has many useful applications that improve the quality of life for everyone in addition to creating the many different colors of nature.


Comments - No Responses to “Rayleigh Scattering”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.