Space mining refers to the planned extraction of mineral content from asteroids, comets, planets, and other heavenly bodies. Astronomers and scientists confirm that a single asteroid could actually hold large amounts of metals and minerals that could amount to billions of dollars in total monetary value. This claimed fact has sparked lots of interest among scientists and businessmen alike. If asteroids hold such large deposits of valuable minerals, investing on mining these minerals from the asteroids could prove to be very profitable. While asteroids could vary in size, it is Read More
Kinetic Hydropower
Kinetic hyrdopower is power created by using turbines under water to collect energy. However, unlike hydrodams that are large, bulky and often times a danger to the ecosystem, kinetic hydropower is an effective way of creating electricity without putting too much of a footprint on the area in which the turbines are installed. How Does Kinetic Hydropower Work? By harnessing the power of the moving water, underwater turbines that are grouped together are able to spin and, with the continuous momentum provided by the water, generate electricity. To make it Read More
What is a Geiger Counter?

A geiger counter is a device that detects (esp. nuclear) radiation by conducting electricity when an ionized particle is present. While geiger counters are not the only devices that detect radiation, they are the most preferred option worldwide due to their portability and low cost. Geiger counters are most often used after environmental and industrial catastrophes that result in some form of radiation leaking into the atmosphere, a water supply, or the ground. How Geiger Counters Work Geiger counters consist of a tube filled with an inert gas such as Read More
What is a Polyolefin?

One of the largest classes of organic thermoplastic polymers is polyolefin. Polyolefin is an odorless, non-polar, and non-porous material that is used in structural plastics, consumer goods, industrial products, and food packaging. Polyolefin means “oil like” and is commonly referred to as a thermoplastic or polyalkene since polyolefin has a waxy texture. This substance is widely used in research and production in the petrochemical and organic chemistry industries. Polyolefin Use in Shrink Wrap Plastic shrink wrap is the lay term for polyolefin. Shrink wrap is designed to expand when heated Read More
What is an Ultrasonic Fogger?

An ultrasonic fogger is a device that uses ultrasonic sound waves to break water into millions of individual water droplets that are then sprayed into the air as a thick fog. Ultrasonic foggers are most often used for Halloween decorations as a dry ice replacement. The fog that an ultrasonic fogger produces is not created through a boiling process and does not involve heat of any kind. Because of this, the fog is cold and slightly wet but poses no threat to the user. How does an Ultrasonic Fogger Work? Read More
How Do X-Rays Work?
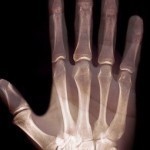
An X-ray is an electromagnetic wave that has a shorter wavelength than visible light and is created when an electrical current passes through an x-ray tube. When the current passes through the tube, the resulting radiation beam is an x-ray. This beam can penetrate objects or materials that consist of light atoms, but objects made of heavy atoms will absorb it. This quality makes X-rays useful for detecting bone fractures and for studying the structure of materials. When were X-Rays Discovered? German physicist Wilhelm Roentgen was the first scientist to Read More
Lightning Detector
A lightning detector is equipment whose main function is to sense lightning during thunderstorms to prevent human casualty and minimize damage to commercial and residential property. Lightning detectors can be classified according to size, capacity and installation location and methods. There are four major categories of lightning detectors and they are the following: Ground-Based Lightning Detection Systems This variant uses multiple antennas separated by hundreds of kilometers to detect the pulses of radio frequency that are produced by a lightning bolt. For this reason, they are often called RF or Read More
What is a Dynamometer?

A dynamometer is a device that measures the power, torque, or force that is being applied to a system or object. Dynamometers also measure how much power, torque, or force is required to perform work within a system. They are used in industrial equipment in order to calculate the amount of power required to operate a machine and moderate power levels in order to prevent accidents that result from too much torque, pressure, or force being applied to an object. How Dynamometers Work Dynamometers work in several ways. The most Read More
What is FTIR Spectroscopy?
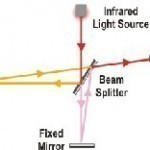
FTIR spectroscopy (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy) is a technique that uses infrared light to observe properties of a solid, liquid, or gas. It is used in many different applications to measure the absorption, emission, and photo-conductivity of matter by shining a narrow beam of infrared light at the matter in various wavelengths and detecting how the matter responds to each wavelength. Once the data has been obtained, it is converted into digital information using a mathematical algorithm known as the “Fourier transform.” How FTIR Spectrocopy Works FTIR spectroscopy is Read More
Radiometric Dating
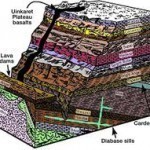
Radiometric dating is a process of identifying the age of a material based on known half-lives of decaying radioactive materials found in both organic and inorganic objects. Radiometric dating is often used to determine the age of rocks, bones, and ancient artifacts. In fact, radiometric dating can be used to determine the age of the Earth, (5.54 billion years old) other planets, and celestial objects. Radiometric dating is often referred to as “radioactive dating” and “carbon dating,” though many different types of isotopes can be used to identify an object’s Read More


Share on: