This FAQ answer is an excerpt from SNIPPETS by Bob Stout. Don't hold your breath. Think about it… For a decompiler to work properly, either 1) every compiler would have to generate substantially identical code, even with full optimization turned on, or 2) it would have to recognize the individual output of every compiler's code generator. If the first case were to be correct, there would be no more need for compiler benchmarks since every one would work the same. For the second case to be true would require in Read More
Scope Resolution Operator

Occasionally, it is useful to distinguish between class member names and other names. The scope resolution operator (::) can be used here. For example class A { private: int x; float y; public: void readm() const; /* ——— ——— */ }; In this class the full name (qualified name) of variable x is A::x. Similarly, the qualified name of y is A::y and the qualified name of readm() is A::readm(). Global Variables and Class Member Variables with the Same Name What Read More
Standard Library Functions
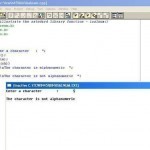
A library is a collection of programs and functions which can be used by other programs. Like all other high-level languages, C++ provides function libraries containing built-In functions. These standard functions are extremely useful to the programmers. The advantages of library functions are listed below: Reusability of code : The program development activity requires three major activities: coding, testing and debugging. If a function is developed previously, then it is available as a standard library function and the effort of redevelopment can be avoided. Faster development : Since many useful Read More
Virtual Base Classes
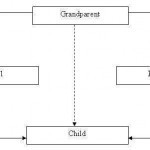
A situation may arise where all the three kinds of inheritance, namely, multilevel, multiple and hierarchical inheritance are involved. This is illustrated in the figure below; the child has two direct base classes 'parent1' and 'parent2' which themselves have a common base class 'grandparent'. The 'child' inherits the traits of grandparent class via two separate paths. It can also inherit directly, as shown by the dotted lines. The grandparent class is sometimes referred to as indirect base class. Such inheritance by the child class may create some problems. All the Read More
Operator Overloading – Introduction
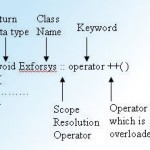
Operators like + (plus), – (minus), * (multiply), / (divide) work very well with data types such as int, float, etc. But when it comes to user defined data types these operators do not work on their own. To make them work, we need to define special functions that tell the operators how to handle the operands of the user defined class. These special functions are known as operator functions. The general form of an operator function is: return_type classname :: operator op(arg) { ——— function body ——— } Where Read More
Jar File

JAR is an abbreviation for Java Archive. It is basically a file in archive format used to group and integrate Java classes, resources, metadata together which can then be easily distributed across Java platform. However the underlying file format is ZIP with a .jar extension. Every JAR file contains a manifest file which is normally the first in the JAR header. The Java Development Kit (JDK) bundles an built-in tool to create and extract JAR files. Like any archive format, JAR also helps compress data that’s packed into it. The Read More
Function Overloading
Function overloading is a concept where several function declarations are specified with a single and a same function name within the same scope. Such functions are said to be overloaded. C++ allows functions to have the same name. Such functions can only be distinguished by their number and type of arguments. Example: float divide(int a, int b) ; float divide(float a, float b) ; The function divide(), which takes two integer inputs, is different from the function divide() which takes two float inputs. What is the need for function overloading? Read More
Java Source Code
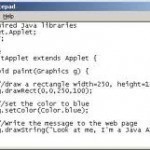
Java source code is code that you write in the Java programming language. Java source code is converted to Java bytecode by the Java compiler. Java source code files usually have the .java extension. Sun recommends that Java source code files be no longer than two thousand lines. Larger source code files should be split up into multiple smaller files.
Selection Sort
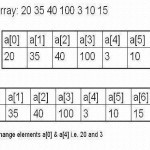
Selection sort requires (n-1) passes to sort an array. In the first pass, we find the smallest element from a[0], a[1], a[2], … a[n-1] and swap it with the first element, i.e. a[0]. In the second pass, we find the smallest element from a[1], a[2], a[3]….a[n-1] and swap it with a[1] and so on. Pass1. Find the location loc of the smallest element in the entire array, i.e. a[0],[1],a[2]…a[n-1]. Interchange a[0] & a[loc]. Then, a[0] is trivially sorted. Pass2. Find the location loc of the smallest element in the entire Read More
Constructors that Allocate Memory Dynamically

Constructors can be used to initialize member objects as well as allocate memory. This can allow an object to use only that amount of memory that is required immediately. This memory allocation at run-time is also known as dynamic memory allocation. The new operator is used for this purpose. Sample Program The program below shows the use of new in constructors of a simple String class. /* * Program to illustrate use of dynamic memory allocation * in constructors * http://www.byteguide.com */ #include #include class String { private: char Read More


Share on: