Pulse Width Modulation, abbreviated as PWM, is a method of transmitting information on a series of pulses. The data that is being transmitted is encoded on the width of these pulses to control the amount of power being sent to a load. In other words, pulse width modulation is a modulation technique for generating variable width pulses to represent the amplitude of an input analog signal or wave. The popular applications of pulse width modulation are in power delivery, voltage regulation and amplification and audio effects. Pulse width modulation is Read More
Siemens (Unit of Electrical Conductance)
The siemens is the standard unit of electrical conductance. It is the inverse of resistance and is equal to one divided by resistance, or current divided by voltage. One siemens is equal to one ampere per volt. History of the Siemens The siemens was defined at an international conference in 1881, and is named after Ernst Werner von Siemens (1816-1892), a German inventor. The symbol for Siemens is a capital S. The previous unit for electrical conductance was called the mho, and it is still used today in some areas Read More
Satellite Launch Sites

Satellite launch sites are facilities on the Earth that are designed to receive and launch satellites that may orbit the Earth or travel to other planets or even star systems. Satellite launch sites are often referred to as “spaceports” or “cosmodromes” and may be situated on ground or in any ocean. While satellites are often launched from facilities that are designed to launch space shuttles and/or rockets, some facilities are entirely dedicated to launching satellites. Although many different companies and organizations own satellites, these companies are not allowed to launch Read More
Walkie-Talkies
A Walkie-Talkie is a portable two-way radio transceiver. A transceiver is a device that has a transmitter and a receiver which are combined together to share common circuitry. A Walkie-Talkie is a handheld communication device and it includes a half-duplex channel i.e. it supports communication in both directions but only one person can transmit at a given instant. However, any number of people can receive the transmitted message. A Walkie-Talkie also feature a push-to-talk switch which is used to switch to the transmit mode from the reception mode. A Walkie-Talkie Read More
Ham Radio
More than three million people enjoy ham radio hobbies, which is basically amateur radio. These enthusiasts create a network of people that enjoy communicating with one another over different frequencies. However, ham radio operators do use a variety of methods to communicate with one another. The amateur radio operators are known as Hams, and they communicate with one another for fun, self-improvement, or even public service. These operators communicate by transmitting messages by voice, Morse code, or even messages through computers. There are some new ways that allow hams to Read More
What is a Multivibrator?
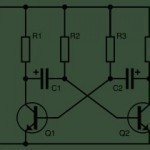
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit that rapidly switches because of positive feedback between multiple states. The switch’s output is harmonic. Three types of multivibrator circuits are used in industry today: astable, monostable, and bistaple. Types of Multivibrators The three multivibrator types are: Astable Multivibrator – The circuit is not considered stable in either of the two possible states. It continually switches from one of the potential states to the other, but does not require a clock pulse or other input in order to operate. Monostable – One of the Read More
Arc Transmitter
The arc transmitter is an instrument for converting direct current into Radio Frequency or (RF) energy. Prior to the development of the arc transmitter, wireless communications were built around the spark-gap transmitter which was inefficient (it wasted bandwidth and used up more energy than required), disruptive (the wide range of frequencies that spark-gap transmitters generated caused massive interference to other radio frequencies), and unstable. The arc transmitter (and later, the high-frequency alternator) was able to focus radio energy along a single frequency (or at least a very narrow frequency range Read More
Satellite Internet
Satellite Internet is an alternative to dialup, ISDN, DSL, or cable Internet. Satellite Internet is extremely interesting to customers who cannot get DSL or cable Internet. Satellite Internet offers broadband speeds, but suffers from high latency due to long round-trip times made necessary by the distance to geostationary satellites. The latency issues related to satellite Internet can be significantly reduced through the use of caches and protocol accelerators. Types of Satellite Internet The two main types of satellite Internet are those in which the return path is sent using dial-up Read More
Crystal Radio
The crystal radio is a rudimentary radio receiver that can be made from a few easy-to-obtain and inexpensive parts. It is unique for this type of radio does not require a battery pack, has no moving parts, and can be built using ordinary household materials, yet it actually works. The only power it receives comes from the radio signals. Radio Broadcasting Basics It should not be surprising that crystal radios work. The basic principles of radio broadcasting make radio crystal operations more than possible. First, the function of a radio Read More
Satellite Systems

The basic types of satellite systems include geostationary (GEO), Low Earth Orbit (LEO), Medium Earth Orbit (MEO), and Highly Elliptical Orbit (HEO) satellites. There are also public and private satellite systems such as Television Receive Only (TVRO), Direct Broadcast Satellite (DBS), Global Positioning System (GPS), and multibeam satellite operations. Geosynchronous satellites orbit the Earth on repeatedly regular points over time. Each GEO satellite is stationary over one spot above the equator and therefore does not need any tracking from receiving and transmitting antennas on the Earth. GEO satellites enable the Read More


Share on: