What is RAID?
RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data reliability and redundancy system that allows data to be stored on multiple computers at the same time. RAID technology is generally used in industrial, commercial, and government computer networks to store copies of system and user files on multiple hard drives that are connected through a logical unit and the network. RAID technology allows companies, agencies, and other institutions to ensure that important files are never lost or that system files that maintain an online server or physical computer network are never corrupted.
How RAID Works
A RAID system is composed of two or more hard drives that are aligned in a single unit and connected to the same motherboard. When RAID technology is connected to a network, computer, server, or other device, that device accesses the RAID system and stores data in any of its hard drives. RAID technology is essentially the same as My Computer in the Windows Operating System, but with additional features that allow data to be copied to all of the unit’s hard drives simultaneously.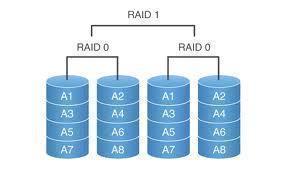
Applications
RAID technology has several applications. It backs up large servers for companies, hospitals, government buildings, schools, organizations, and other institutions. It ensures that important personal, commercial, and system files are not lost due to system failure, viruses, or even accidental removal. While RAID technology is almost always used exclusively for commercial or industrial purposes, RAID systems can be used domestically in order to backup a personal computer or website.
Advantages
RAID technology allows data to be stored on multiple hard drives at the same time, therefore ensuring data reliability. RAID systems are relatively small, can operate on plug-and-play technology, and have high data transfer rates for storing and accessing files. Also, RAID technology can either be directly connected to an administrative device or to a wireless or Ethernet-based network.
Disadvantages
RAID systems are generally expensive and significantly heavier than single hard drives. RAID technology should be connected to a device through a surge protector due to the fact that a power surge could destroy all of the hard drives at once. This is because the hard drives in a RAID system are all connected and power spikes in any easily affect the others.


Comments - No Responses to “What is RAID?”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.