Automatic gain control is a technique implemented in many consumer electronics that automatically adjusts the input levels of a system by inducing a portion of the output levels in the input terminals. Automatic gain control is used in a wide variety of technologies, including telecommunications, navigation, audio/video recordings, and radio systems. Automatic gain control can also be seen in biological systems, such as the vertebrate visual and audio systems. How Automatic Gain Control Works Automatic gain control is dependent on a loop in which the output terminals of a Read More
Banana Plugs
A banana plug is mainly used to insert speaker wire coming from an amplifier or receiver directly into the speaker. The banana plug is named after its shape. It is a slender, but bulging prong that is similar to a banana. However, unlike bananas, the banana plug is not bent, but straight. Other uses for the banana plug is to test electronic equipment – specifically used to terminate patch cords. It should be noted that the banana plug is the male version and the banana jack is referred to the Read More
SHN
SHN is a .wav file compression process that helps to improve the way audio source files are stored. The following is some background on the concept of SHN and some suggested applications. What SHN does SHN is used in audio compression processes. The idea behind SHN (or Shorten) is to compress an audio .wav file without losing any type of data associated with the source file. This can be contrasted with the MP3 file, which usually discards some information associated with the source file; this lost information cannot be recovered Read More
How Long Audio Cassette Tapes Last?
Predictions regarding the demise of audio tapes have been coming thick and fast over the past 20 years. When the first CDs came onto the market, it was easy to predict that the popular cassette tape was ready for the dumpster. Now, some 20 years later, the cassette tape is still being produced in solid numbers. Sure, the music market for the magnetic tape is pretty much gone, but other markets, such as spoken language tapes, continue to see strong sales. Simple and Durable KISS applies well to the cassette Read More
Lossless Compression
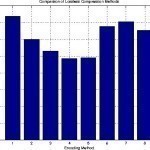
Lossless compression is any compression format where all information in the imput stream is preversed in the output stream. Audio Formats which use Lossless Compression Lossless compression is less commonly utilized in computer audio file formats than lossy compression. Audio file formats which use lossless compression include: Free Lossless Audio Codec (FLAC) ALAC Direct Stream Transfer (DST) Monkey’s Audio APE RealAudio Lossless Shorten (SHN) The True Audio (TTA) WavPack lossless WMA Lossless Lossless Compression vs. Lossy Compression The alternative to lossless compression is lossy compression. Lossless compression yields smaller output Read More
Audio Data: Tag 8192
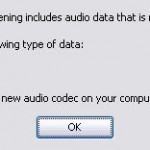
If you are a Real Player audio user who wants to download a file or play some audio or audio-video file and all code programs are not present, you may receive an error message “Audio Data: Tag 8192”. Naive computer users and people who are not really technically savvy would usually find the error message odd and if you are not really into it and try fixing the problem by changing the settings in your divx, musicplayer or real player program. If you do this, chances are you might end Read More
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec)
FLAC (Free Lossless Audio Codec) is an audio format similar to MP3, but it is a lossless encoding format, meaning that audio is compressed in FLAC without any loss in quality. FLAC is unique as it is the fastest and most widely supported lossless audio codec, and the only one that at once is non-proprietary, and is not patented. It has an open-source reference implementation, and is a well documented format and API, and has several other independent implementations. Being a lossless compression format, FLAC does not remove any data Read More
Who Invented the Microphone?

A microphone is a device that converts acoustic power into electric power. Both the acoustic power and the electric power have similar wave characteristics that convert sound waves into electric voltages that eventually convert back into sound waves through speakers. Microphone were used with the first telephones, and then with radio transmitters soon after. Sir Charles Wheatstone was the first person to come up with the word “microphone” in 1827, but even so, it was Emile Berliner who invented the first microphone in 1876. Emile Berliner was born in Hanover, Read More
Free Music Editing Software
Though there are several free music editing software packages available, a software utility entitled Audacity is very robust and has a version for Mac, Linux, and PC. Audacity can record live audio via mixer or microphone, as well as digitally capture recordings from cassette tapes, vinyl records, or mini-discs. Depending on your sound card, Audacity can also grab streaming audio, and you can create multi-track recordings by dubbing over already existing tracks. Provided that you have multi-channel hardware, Audacity will allow you to record up to 16 hardware) channels at Read More
High Definition Audio
High Definition Audio, also known as HD Audio, is an audio standard created by Intel to be used on their chipsets, i.e. it is a standard for high-quality on-board audio. HD Audio was designed to replace the Audio Codec 97 (AC'97) standard that Intel released in 1997. The main achievement of the AC'97 specification was the audio quality improvement in popular sound cards by complete separation of analog and digital sections, and the raise in maximum playback sample frequency up to 48 kHz for compatibility with the audio format in Read More


Share on: