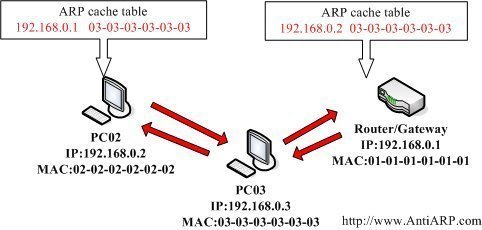
ARP Cache
The ARP cache is a table that stores mappings between Data Link Layer addresses and Network Layer addresses.
The Data Link Layer addresses are usually MAC addresses and the Network Layer addresses are most frequently IP addresses.
The Operating System stores the ARP cache in RAM.
Displaying the ARP Cache
Under most Unix and Microsoft Windows versions, the command `arp -a` displays the ARP cache.
Unix ARP Cache Example
$ arp -a
www.byteguide.com (192.168.1.2) at 00:34:c4:45:73:21 on fxp0 permanent [ethernet]
fw.byteguide.com (192.168.1.1) at 00:34:62:a1:c2:00 on fxp0 [ethernet]
Microsoft Windows ARP Cache Example
C:>arp -a
Interface: 192.168.1.101 — 0x80004
Internet Address Physical Address Type
192.168.1.1 00-0d-6d-bc-a8-6b dynamic
192.168.1.2 00-0e-1c-2b-e5-3c dynamic
Further Reading on the ARP Cache
To learn more about the ARP protocol, read What is ARP?
To learn how to clear the ARP cache, read How do I clear the ARP cache?


Comments - No Responses to “ARP Cache”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.