VPN (Virtual Private Network)
VPN
A VPN (virtual private network) gives the end-user a secure means of connecting to a remote network over a remote or public Internet connection. The remote network can either be a private LAN such as those used at businesses, schools, the home, or one providing remote services to the user. The best way to conceptualize a VPN is that it creates a virtual tunnel through the Internet to the private network resource(s) located at the opposite end of the connection. The network traffic over the VPN is encrypted providing an additional layer of security and privacy for the computer user.
What are the Types of Virtual Private Network Architecture?
When VPNs were first created, they used a remote connection over a leased-line or dial-up modem to connect to the remote server. These early VPNs used ATM virtual circuits typically provided by commercial entities such as AT&T or Verizon. Today, VPNs are based on multi-protocol label switching networks (MPLS) which use modern networking technology to facility the service. Along with the high-speed Internet speeds realized with today’s modern fiber-based networks, the cost to use a VPN has significantly decreased over the past decade.
The two primary types of virtual private network architecture in use today are network-to-network connections or as a remote access type for end-users. The remote access VPN allows end-users to access
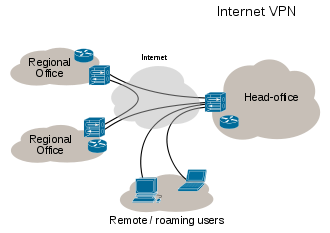
VPN Connectivity overview.
personal, work, or school resources while away from the office or school by making use of the VPN. The network-to-network VPN architecture allows organizations to share resources across disparate geographic locations without having to create redundant infrastructure at multiple sites. A more recent use for virtual private networks has been to use an IPv4 network to connect two or more IPv6 networks!
How Are VPNs Classified?
There are several methods that are used to classify virtual private networks. These include:
1 – By the termination location of the network.
2 – The VPN protocol used by the server.
3 – Degree of security provided by the VPN.
4 – Whether the network allows remote access by end-users or is designed to provide connectivity between networks.
5 – The OSI Layer (networking layer) used for network presentation when trying to connect to network services.
VPN Protocols
The largest advantage to using a VPN is that it provides a secure connection over the public Internet between the end-user (or network) and a private network. In the modern-working era, it has almost become essential to provide this type of access to organizational resources to consumers who are away from the home office or school. Additionally, a number of home computer users have found it advantageous to leverage the strengths of VPN services to provide an added layer of security when going online. There are several widely used VPN protocols in the market today to include: L2TP, PPTP, SSL, and IPSec.
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol)
L2TP is a network tunneling protocol that supports virtual private networks. It does not provide encryption; instead L2TP relies on the PPP (Point-to-Point protocol) to provide encryption of network traffic. The protocol was created by Cisco and Microsoft and provides data integrity and data confidentiality for traffic sent to/from a VPN implementing the protocol. L2TP was published as a proposed standard, RFC 2661, in 1999. L2TP tunnels can be extended across a full PPP network session, or across a single segment of a two-segment networking session. The four network tunneling models used by the protocol are:
1 – A Voluntary tunnel.
2 – Compulsory tunnel, remote dial.
3 – Compulsory tunnel, incoming call
4 – L2TP muti-hop network connection
PPTP (Point-To-Point Tunneling Protocol)
The Point to Point Tunneling Protocol (PPTP) is one of the most widely used and supported VPN protocols for the Windows Operating System. The protocol was originally created by the Microsoft Corporation in cooperation with other companies and makes use of a control channel over the TCP protocol while using a GRE tunnel to encapsulate PPP network packets. PPTP is generally considered one of the fastest VPN protocols and can be used on Mac or Linux computers.
There have been a number of security studies made on the PPTP standard since it has been in wide-spread use. The majority of the vulnerabilities found in the protocol originate with the PPP authentication used in PPTP along with the integration between the underlying MPPE and PPP authentication for session key establishment with new connections. As a result, Microsoft no longer recommends use of the protocol; however, it remains in use by many VPN services at the time of this writing.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
The SSL VPN provides VPN access via the https protocol through a web browser. The primary advantage of the SSL protocol is that you do not have to do any network configuration on the client computer to connect to the VPN. Additionally, user access can be restricted to very specific services or applications on the server unlike traditional VPN access. A major disadvantage of the protocol; however, is that it relies on the web browser for access. This takes away some of the anonymity that some consumers prefer when using VPN services.
Layer 2 Forwarding (L2F)
Layer 2 Forwarding is an IPsec protocol used for encryption along with the L2TP tunnel. It is used to encrypt and authenticate all IP packets sent over a VPN connection in order to provide a secure connection. A major disadvantage of the protocol is that it requires major client-side installs which can prove too costly in both time and sometimes money for many VPN users.
Common Reasons to Use a VPN
There are a number of reasons to choose to make the shift to using a virtual private network. These range from just needing to access the local network at school or work at home, accessing your home network while on the road, or to increase your browsing security and anonymity while in public places.
Improved Internet Browsing Security
As more and more end-users and services rely on the Internet, the threat from malicious actors continues to increase. As a result, one of the primary advantages to using a VPN is the improved security it provides to end-users who choose to conduct work or other tasks at home or on the road. Since a VPN creates a virtual tunnel between the virtual private network and the user’s computer, activity has an added layer of encryption to prevent exploitation by those who sniff unencrypted network traffic.
Provides Improved Quality of Life for Expats
One of the biggest disappointments for new expats once they move overseas is not being able to realize the same quality of service for home-based Internet services such as online television (BBC Sky, Netflix, FOX, ABC, etc.) and increased costs for VOIP and video services such as Skype and Google Voice. Many will attempt to use a proxy based in their home-country at first to see the same quality of service; however, quickly get disappointed. By using a VPN service based in one’s home country, you are able to obtain the same access to television programs and services such as Netflix which restrict out-of-country access as well as pay the same price for VOIP services as if you were home.
Provides a Virtual Firewall for Smart Phones/Tablets
In the recent past, the majority of smart phone and tablet manufacturers have made it possible to connect to VPN services from the device(s). As a result, it has become more popular with mobile users to subscribe to a VPN to use on the laptop at home as well as on their smart phone while away from the house or apartment.
Stay Anonymous on the Web
The majority of virtual private network providers allow end-users to use the service to surf the Internet without providing the client-computer’s IP address to the website(s) being visited. Not only does this allow the consumer to enjoy a higher quality of service (potentially), but it also permits surfing without worrying about one’s IP address being tracked by each and every website, ad server, and Google. It also prevents potential malicious actors from recording your IP address to use in potentially nefarious schemes. Although most sites/advertising agencies claim the IP recording is simply to improve end-user experiences online, many prefer to keep this information from being provided to external organizations.
Improved Public WiFi Security
There seems to be a pubic WiFi connections available just about anywhere you go in today’s world. Unfortunately, many end-users do not realize that network traffic sent over these connections is unencrypted and poses a potential security risk to user account login and password information. There are a number of publicly available scripts on the Internet that allow “Script Kiddies” to capture logins and passwords on public WiFi networks if the targeted computer is using unencrypted network connection(s) to sign-in to private accounts. When connected to services over a VPN, the traffic is encrypted which encourages these rogue actors to move on to softer targets when attempting to steal person information.
Better Security than Proxies
Even though proxies and VPNs are similar in that end-users are able to surf the Internet without their computer’s IP address being provided to websites, they are functionally different. Proxy operations are similar to web filters. When using a proxy, the Internet traffic generally flows from the user’s web browser to the proxy and on to the Internet making use of the browser’s proxy stings. If one is using other Internet-based services on a computer, they will not be sent to the proxy server. A virtual private network; however, encrypts all network traffic from the client computer once connected to the VPN. Additionally, computer users can disconnect or connect to the VPN service from the client computer depending on one’s needs. Since proxy servers are based on using an Internet browser, they may not support non-browser functions such as Google Voice or Skype.
Can Provide Static IP Services
An increasingly common usage of a VPN is to take advantage of static IP address services offered by some service providers. Many companies/end-users have found it beneficial to leverage static IP’s to provide another layer of security when accessing school or company-based web services.
How to Choose a VPN Service
There are several capabilities you can consider when making the decision to pick a VPN service. Depending on individual needs, some of these capabilities may be more important than others.
#1 – Where the VPN Servers are located
This is one of the often overlooked factors for new expats who want to make use of VPN services. For example, if you are from the United Kingdom and currently working in Dubai, you will want to use a VPN based in the UK to take advantage of home-based Internet services. Similarly, if you are from the United States, then picking a VPN server based in another country will not likely provide you the quality of service you desire from the VPN.
#2 – VPN protocol used by the Server
Many of the high-end VPN services on the market will offer one or more of the commonly found VPN protocols to end users. These include: L2TP, PPTP, SSL, and IPSec. Depending on your reasons for signing up for a VPN, you may or may not choose to prioritize speed over security with the protocol you choose.
#3 – Your bandwidth requirements
Although many services will offer unlimited bandwidth today, there are still a number of service providers who will require a larger monthly payment to have more bandwidth. If simply using the service to provide an added layer of security to normal computer usage, you can likely afford to have a smaller bandwidth cap. If using a VPN to watch television or movies while abroad, then you will want to consider one of the unlimited services.
#4 – Does the service allow Torrent/P2P traffic?
With the number of RIAA lawsuits over the past decade relating to P2P traffic and music downloading, many VPN companies will not allow either the Torrent or P2P protocols to be used on their web servers. If you make use of a file sharing service, ensure you verify if the protocols are supported by the VPN before signing up for a service.
#5 – Does the VPN offer a trial period or money-back guarantee?
Not all VPNs are created equal. You should always be suspicious of a VPN which doesn’t at least offer a money-back guarantee before providing your credit card or other private information required to subscribe to a service.
#6 – Level or degree of security offered by the VPN
VPNs use different protocols and provide different levels of security for the end-user. If you are signing up for a service to increase the security of your Internet surfing, then you will want to prioritize these capabilities over speed and bandwidth if required.
#7 – How much does the VPN service cost a month?
For non-commercial users, monthly cost is a huge factor. Be hesitant to sign-up for a VPN service which is extremely cheap as compared to other major service providers as you may be signing up for a reseller service and not realize sufficient quality of service.
#8 – How reliable is the VPN service?
VPN reliability can change based on a number of factors to include: growth, maintenance, and geographic location to the end-user. If signing up with a new service provider, they may not have the infrastructure in place to handle growth so make sure you do your research before picking a VPN service.


Comments - One Response to “VPN (Virtual Private Network)”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.