Understanding ISA Server Client Types
ISA Server Client Types Overview
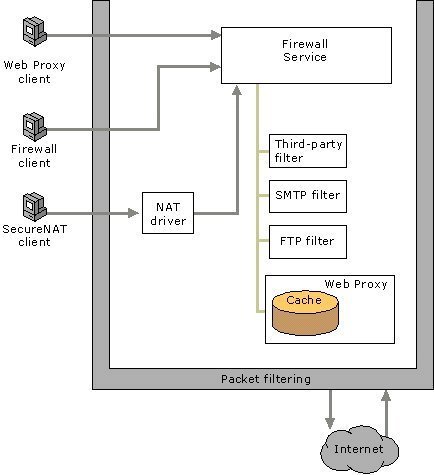
The different ISA Server client types are:
Firewall client: These are client computers on which Firewall Client software is installed and enabled.
- SecureNAT client: These are client computers that have no Firewall Client software installed and enabled.
- Web Proxy client: These are client Web applications which are set up to use the ISA Server computer.
You have to consider the needs of the organization before you install any client software:
- You have to determine which applications and services your internal clients need to access.
- You next have to determine the way in which servers will be published.
- Then, you can determine which ISA Server client types to install and configure to meet your requirements.
When determining client requirements, you have to include the following:
- Client needs.
- Authentication requirements.
- Network infrastructure.
Web Proxy clients and Firewall clients are the only client types that can pass authentication information to ISA Server.
If your ISA Server computer is already a member of a domain, you can use Windows 2000 or Windows Server 2003 security groups and accounts for authentication. For standalone ISA Server computers, the account database can be used.
A few recommendations for determining ISA Server client types are listed here:
- If you do not want to deploy client software and configure your client computers, then the recommended client type is the SecureNAT client. SecureNAT clients need no additional software installed, nor do they need a specific configuration. Firewall Client software is not installed for SecureNAT clients.
- If ISA Server is being used for forward caching of Web objects only, then the recommended client type is SecureNAT client. Client requests will be forwarded transparently to the Firewall service of ISA Server, and then passed to the Web Proxy service.
- If you want to publish servers located on the internal network, the recommended client type is SecureNAT client. You can publish internal servers as SecureNAT clients. All you need to do is create a server publishing rule on ISA server.
- If the network supports roaming computers and users, then you have to use the Firewall Client type. This is mainly due to SecureNAT clients not supporting automatic discovery of ISA Server. With automatic discovery, Firewall clients and Web Proxy clients automatically discover the ISA Server computer to use.
- If your organization needs to define user based access rules to control non-Web Internet sessions, then the recommended client type is Firewall Client. User based access rules can be created for Web Proxy clients on Firewall client computers and SecureNAT client computers. Rules are implemented only when ISA Server is set up to require Web applications to provide authentication information with sessions.
- If your organization needs to support dial-on-demand for non-Web sessions, then you must use the Firewall Client. This is the only client type that actually supports dial-on-demand for non-Web sessions.
- If clients need access to protocols with secondary connections, then you must use the Firewall Client type. SecureNAT clients include no support for this type of configuration.
Firewall Client Overview
A client is considered a firewall client if it has Firewall Client software installed and enabled. ISA Server Cache mode does not support the firewall client type. Firewall clients run Winsock applications that utilize the Firewall service of ISA Server. Firewall Clients software is usually installed from a network installation share.
You can install Firewall Clients software on all Windows operating systems.
When a firewall client requests an objct from a computer, the firewall client actually first determines the location of the object. The client does this by checking its copy of the local address table (LAT) of ISA Server.
For objects that are located on computers that reside in the internal network, the client then accesses the computer directly. If the computer is not in the ISA Server LAT, the request is forwarded to the ISA Server Firewall service. The ISA Server Firewall service then forwards the request to the destination, based on whether the request is allowed. Firewall clients support user-level authentication.
When Firewall Client software installed, the following components are installed:
- mspclnt.ini; is the client configuration file and copy of the local domain table (LDT).
- msplat.txt; is the copy of the local address table (LAT).
- Firewall client application.
The Firewall Client configuration entries that are added in the configuration file for a Winsock applications are listed here:
- Disable; values are 0 or 1. A value of 1 indicates that the ISA Server Firewall service is disabled for the application.
- NameResolution; values are R or L. The default setting redirects Internet domain names to the ISA Server computer. Other names are resolved at the local computer. A setting of L results in all names being resolved at the local computer. A setting of R results in all names being redirected to the ISA Server computer for name resolution.
- LocalBindTcpPorts; defines a TCP port, list, or port range which is bound locally.
- LocalBindUdpPorts; defines a UDP port, list, or port range which is bound locally.
- RemoteBindTcpPorts; defines a TCP port, list, or port range which is bound remotely.
- RemoteBindUdpPorts; defines a UDP port, list, or port range which is bound remotely.
- ServerBindTcpPorts; defines a TCP port, list, or port range for all ports that should allow multiple connections.
- ProxyBindIp; defines an IP address or list used when binding with a corresponding port.
- KillOldSession; values are 0 or 1. When set to 1, and the ISA Server computer keeps a session from an old instance of an application, the session has to be terminated before the application can establish a new session.
- Persistent; values are 0 or 1. When set to 1, the ISA Server computer maintains a specific server state.
- ForceProxy; forces a specific ISA Server computer for a particular Winsock application.
- ForceCredentials; a value of 1 forces the use of alternate user authentication credentials which are stored locally on the computer.
- NameResolutionForLocalHost; defines how the local client computer name is resolved.
- ControlChannel; defines the control channel type used.
SecureNAT Client Overview
A client computer is considered a secureNAT client when:
- It has no Firewall Client software installed.
- It can connect to the Internet through the ISA Server.
ISA Server Cache mode does not support the SecureNAT client type. SecureNAT clients are supported on operating system that supports Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/ IP). SecureNAT clients also require ISA Server application filters to access the Internet.
You have to ensure that the default gateway for SecureNAT clients is configured correctly. When configuring the default gateway for the SecureNAT clients, you have to take into account the network topology. In a simple network topology, routers are not configured between the SecureNAT client and the ISA Server computer. A complex network however has one or multiple routers that connect multiple subnets configured between SecureNAT clients and the ISA Server computer.
A few benefits of using the SecureNAT client type are listed here:
- You can use ISA Server applications filters to access complex protocols.
- Almost all access control features are supported.
- Caching of HTT requests provide fast retrieval.
Web Proxy Client Overview
The Web Proxy service is a Windows service that supports requests from Web browsers, and thereby provides Web access for:
- Windows.
- Macintosh.
- UNIX with Web access.
The Web Proxy service supports the use of the following protocols:
- Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP).
- Gopher protocol.
- Secure HTTP (S-HTTP) for SSL connections.
You have to configure Web Proxy clients to use the ISA Server computer. To do this, you can use one of the following approaches:
- Manually configure each client browser to use the ISA Server computer.
- Define automatic configuration for firewall clients by using the ISA Management console.
- Manage Web proxy configuration through Group Policy I.E. settings.
- You can configure DHCP servers and DNS servers to provide Web proxy Autodiscovery Protocol (WPAD) in cases where ISA Server does not respond to client requests directly.


Comments - No Responses to “Understanding ISA Server Client Types”
Sorry but comments are closed at this time.