Timekeeping devices usually contain or are connected to a machine that swings back and forth or oscillates at a constant rate to control the movement of hands or the rate of change of digits. Mechanical or analog clocks use balance wheels, pendulums and tuning forks as well as quartz crystals as their oscillating machinery for time measurement. Atomic clocks operate in much the same way – except that they use the frequency of the oscillation of atoms or molecules to measure time – thus the name 'atomic clocks'. How an Read More
Fine Structure Constant

The Fine Structure Constant is a constant in theoretical physics that determines the strength of the interaction between two opposing electromagnetic waves. The Fine Structure Constant is used for a wide variety of purposes, but is entirely hypothetical and does not depend on any real units of physics. For example, the Fine Structure Constant can be used to determine the displacement of a beam of light as it comes in contact with a radio wave or vice versa. How the Fine Structure Constant Works The Fine Structure Constant is defined Read More
What is Malleability?

Malleability refers to metals’ (and other hard materials’) ability to be stretched, shaped, or molded through applied pressure. While not all objects are malleable, most metals are. This is the reason that metals such as gold, silver, and platinum, are used to make jewelry and electronic circuits. Malleable objects can usually be reshaped and molded around other objects when pressure is applied to them via a hammer or roller. How Malleability Works Physical changes in metal are responsible for its deformation. When a malleable metal is compressed, individual molecules Read More
Teleportation
In 1931, Charles Fort, an American writer, tried to describe the random disappearances and appearances of different anomalies. He felt that these sudden disappearances and appearances were connected and therefore felt that they were "teleporting." While he came up with this theory to try and explain why certain paranormal phenomena acted, many suggest that Fort probably didn't subscribe to the theory and was using it as a way of suggesting mainstream science didn't provide enough information on why these phenomena happened. Dematerialising This is the transmission of data from one Read More
What is Bioluminescence?

A living organism is bioluminescent when it produces and emits light. Most organisms that do this live in the sea. However, there are several land insects and plants that also have bioluminescent qualities, including the firefly. The trait has typically evolved in organisms that either need to communicate with each other or lure/detect prey. How does Bioluminescence Work? Light is created when an electron orbits an atom’s nucleus. When an electron receives enough energy to jump to a higher orbital shell then falls back to the lower shell, the resulting Read More
Daylight Savings Time

Daylight Savings time, or Daylight Saving Time, is the process of adjusting the clocks twice a year to add more daylight time in the afternoons and less in the mornings. Daylight Savings Time has undergone many changes and thrown under much controversy in its history but it remains a vital part of our society today, all around the world. In this article, we will go over how Daylight Savings Time started, how it works, the pros and cons, and how Daylight Savings Time effects computers. Origins and History Daylight Savings Read More
What is Magnetic Wire?

Magnetic wire is a copper or aluminum wire that produces an electromagnetic field when wrapped into a coil and connected to a power supply. It is used in a number of applications and is a vital component in many different devices. Magnetic wire can be used in electrical to electrical, electrical to mechanical, and mechanical to electrical systems, each of which derives its own specific function from magnetic wire. How Magnetic Wire Works Magnetic wire is generally made of either copper or aluminum, although copper produces much better results with Read More
The Peltier Effect
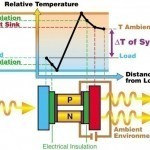
The Peltier effect is one of the three separately identified effects to which “Thermoelectric Effect” or simply, “Thermoelectricity” refers. The other two are the Seebeck and Thomson effects. Discovery This effect is named after French physicist Jean-Charles Peltier, who discovered it in 1834. Peltier found that the junctions of dissimilar metals were heated or cooled depending on the direction of electric current flow through them. The heat that the flow of current in one direction generated was absorbed if the direction of current was reversed. Peltier inadvertently discovered this while Read More
Harmonic Balancer

A harmonic balancer is a device that is connected to an engine’s crankshaft in order to reduce any vibration’s negative impact on the crankshaft and to dissipate the energy that shaft rotation creates. Since the device is the engine compartment’s first element that is connected to the shaft, it absorbs the majority of the energy generated during engine use. By absorbing this energy, only the harmonic balancer (instead of more vital engine components) fails, thereby preventing catastrophic engine failure. How does the Harmonic Balancer Work? The harmonic balancer is made Read More
Dielectric Constant
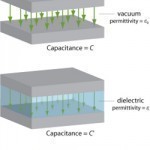
A dielectric constant measures the extent that a material concentrates electrostatic flux and is also known as the relative static permittivity, static dielectric constant, and relative dielectric constant. It is essential when determining if a substance can be used in a capacitor or various chemistry and physics applications. A material’s dielectric constant value must be known before using it to make optical fibers or coaxial cables. Although the term is commonly used, it may have different mathematical connotations depending on the context of its application. The dielectric constant refers to Read More


Share on: