Holographic memory is a storage device that is being researched and slated as the storage device that will replace hard drives and DVDs in the future. It has the potential of storing up to 1 terabyte or one thousand gigabytes of data in a crystal the size of a sugar cube. Brief History of Holographic Memory Using holograms as memory storage was first proposed by Pieter Heerden in the 1960s. During the early 1970s, a group of scientists from TRCA laboratories succeeded in storing 500 holograms using an iron doped Read More
Laser Engraver
As its name suggests very clearly, laser engraving is the art of engraving or marking objects using one or multiple lasers. Considering the preciseness that is required with the engraving, the whole process is quite complex and technical, which often requires a computer. Therefore, as desired, the final engravings are done extremely precise at a very high rate. Most of the laser engraving done today is conducted by what is known as a laser engraving machine. This machine has three main parts to it: a laser, a surface, and a Read More
How Overhead Projectors Work

Overhead projectors work with the help of transparencies. All data are printed on top of the transparencies. Before starting up, be sure to have a socket with live electricity where you can switch the overhead projector. The power buttons are usually made of first class plastic, the “click” sound is heard; it means it has been successfully put “on”. If the overhead projector is not working, try to push the button more slowly, and you can feel the “click”. Inside the overhead projector, usually it is like a television, but Read More
How Do Lasers Work?
Lasers have revolutionized the way that many devices and machinery work. From CD players to machines that cut metal, lasers play an important part in many daily activities, right under the noses of unaware consumers. Lasers are used in dental drills, tattoo removal, hair replacement, eye surgery, and there is now even a method of using laser beams to create rain. While some lasers are harmless, others are extremely dangerous and not all lasers are the same. However, all lasers work in pretty much the same way. This article will Read More
How a Laser Level Works
As its name suggests, a laser level is a leveler that illuminates a horizontal plane using a laser. It was originally developed by an inventor named Steve Orosz. The laser level works by being stationed on a tripod. This projector also has a rotatable head with a mirror, so that the laser beam can also sweep across the vertical axis. It is adjusted through the many visually interpretable level vials and the numerous screws that must be manually adjusted by a human for correction projection. Then, a staff with an Read More
How Fiber Optic Cables Work
There are two main types of fiber optic cable, which are single mode and multi-mode. Single mode: Single mode fiber optic cable is a narrow strand that only has one mode of transmission. Single mode fibers are able to transmit at high speeds over long distances as a result of their small core. Because single mode fiber optic cable provides longer transmission distances and faster transmission rates than multi-mode fibers, it costs more than fibers that are multi-mode. Multi-mode: The reason that multi-mode has a lower cost than single mode Read More
PIR Sensor

A PIR (Passive Infrared) sensor detects infrared light that is emitted from objects within its field of view. PIR sensors differ from other infrared sensors because they can only receive infrared waves. Because all objects emit infrared waves (electromagnetic waves that travel with heat), PIR sensors can detect objects that are in front of them. In fact, PIR sensors can detect many things that humans cannot. PIR sensors are used in many applications, such as night vision, motion detection, and laser range finding. How PIR Sensors Work PIR sensors are Read More
How Fiber Optic Lights Work
Fiber optic lines, which can be as thin as a piece of human hair, are made of strands of glass that are optically pure. They are used to transmit light signals, and have the ability to carry these signals over long distances. How is Light Transmitted Through Fiber Optics? The process by which light is transmitted through fiber optics can best be described through the use of an analogy. If you want to shine a light through a tunnel, you can do so by pointing a flashlight down the tunnel Read More
What is a Diopter?

A diopter is a lens that bends light in order to magnify an object. Diopters can be used to enlarge small objects or see across far distances and are generally integrated into other objects in order to maximize efficiency and accessibility. A diopter can also refer to a measurement that describes a lens’s optical power and measures the maximum distance that a lens is capable of viewing an object from. How Diopters Work A diopter (lens) is a transparent piece of glass or plastic that bends light inward or outward Read More
What is Index of Refraction?
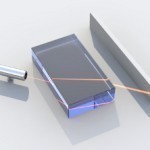
The index of refraction (refractive index) is a measurement of the speed of light in a medium compared to the speed of light in a vacuum. Since light travels at different speeds in different materials, it may change its direction. For example, the index of refraction for water is 1.33, meaning that light travels 1.33 times as fast in a vacuum as it does in water. This is why light bends when it comes in contact with the surface of water. Likewise, light travels at different speeds through materials at Read More


Share on: