CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection) is the protocol used in Ethernet networks to ensure that only one network node is transmitting on the network wire at any one time. Carrier Sense means that every Ethernet device listens to the Ethernet wire before it attempts to transmit. If the Ethernet device senses that another device is transmitting, it will wait to transmit. Multiple Access means that more than one Ethernet device can be sensing (listening and waiting to transmit) at a time. Collision Detection means that when multiple Read More
ARP Cache
The ARP cache is a table that stores mappings between Data Link Layer addresses and Network Layer addresses. The Data Link Layer addresses are usually MAC addresses and the Network Layer addresses are most frequently IP addresses. The Operating System stores the ARP cache in RAM. Displaying the ARP Cache Under most Unix and Microsoft Windows versions, the command `arp -a` displays the ARP cache. Unix ARP Cache Example $ arp -a www.byteguide.com (192.168.1.2) at 00:34:c4:45:73:21 on fxp0 permanent [ethernet] fw.byteguide.com (192.168.1.1) at 00:34:62:a1:c2:00 on fxp0 [ethernet] Microsoft Windows ARP Read More
DSL Modems
A DSL modem is a device that is used to connect a computer to a DSL phone line. It is a type of transceiver whose purpose it is to both transmit information as well as receive information. In other words, it is the central hub of the Internet in an individual's home. Typically, a DSL connection can provide the user with the ability to transmit information from anywhere between hundreds of kilobites per second up to many megabites per second. On top of that, the frequencies for a DSL connection are Read More
DSL Filter
A DSL filter is an analog device that improves a DSL connection by minimizing telephone signal interference with the DSL system. When installed, it acts as a barrier to prevent low frequency telephone signals to interfere with the high frequency ADSL system and vice versa. How DSL Filters Work Telephone signals usually range from 300 to 3400 hertz, while ADSL systems use frequencies between 25 KHz and 1.1 MHz to carry fast data traffic. Both signals are present and they pass through the same copper wire. With both signals working Read More
How to Change a MAC Address
Every Ethernet card had a factory assigned MAC address burned into it when it was made. At times, users may want to change this MAC address to one of their choice. One of the main reasons for doing this is to get around access control lists(s) on a specific router or server, either by hiding a certain device on a network or by allowing it to mimic another network device. The procedures for changing a MAC address are specific to each operating system. How to Change a MAC address in Read More
What is VDSL2?

VDSL2 is an acronym which stands for Very High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line Generation 2. This is based on of the original Very High Bit Rate Digital Subscriber Line (VDSL) but runs on a different frequency (30 MHz) over 7 different bands to produce extremely high bandwidth capabilities. The service for VDSL2 is available in many different parts of the world and can be accessed through the copper wire phone lines that are already in place. This makes it extremely easy to get a fast connection which is available Read More
Tunneling
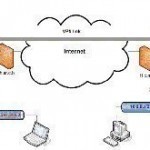
Tunneling is a way in which data is transferred between two networks securely. All the data being transferred is fragmented into smaller packets or frames and then passed through the tunnel. This process is different from a normal data transfer between nodes. Every frame passing through the tunnel will be encrypted with an additional layer of tunneling encryption and encapsulation, which is also used for routing the packets to the right direction. This encapsulation would then be reverted at the destination with decryption of data, which is later sent to Read More
DSL (Digital Subscriber Line)

Digital Subscriber Line or Digital Subscriber Loop (DSL) is a type of high-speed Internet technology that enables transmission of digital data via the wires of a telephone network. DSL does not interfere with the telephone line; the same line can be used for both Internet and regular telephone services. The download speed of DSL ranges between 384 Kbps and 20 Mbps. The most popular implementation of DSL today is Asymmetric Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL). It is asymmetric because the upload and download speeds are not the same (not synchronized). Upload Read More
ADSL Modems

Description of ADSL A special Internet service which is available in many areas is called the Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line (ADSL). ADSL connections use existing copper telephone lines to transmit data to and from the ISP. These connections may be limited by proximity to the ISP or the telephone company because the data will lose strength through the phone lines the further away it is to where it needs to travel. Usually, these services require a special type of ADSL modem to access the Internet at high speeds usually within 1.5Mbps and 9.0Mbps. This Read More
Differences Between ISDN and DSL
Definitions Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN): ISDN is a digital transmission system, which is used to transmit voice and data through copper telephone wires. In other words, it's a circuit-switched data transmission system that is used for voice and data transmission over the wire. Digital Subscriber Line (DSL): DSL is also a digital transmission system and utilizes already installed copper wires to send voice and data packets. Differences As far as the differences between ISDN and DSL transmission system are concerned, there are several differences one can find: Speed In Read More


Share on: