A circuit simulator is a computer program that predicts how electronic circuits work. Circuit designs are first entered through the schematic editor, then the simulation engine solves the complex equations that govern circuit behavior. Circuit simulators are especially useful for designing integrated circuits that are impractical to prototype using breadboards. The three types of simulator are analogue, digital, and mixed mode. Schematic Editor Early schematic editors were text-based and difficult to use, but modern editors have a graphical interface that allows designers to drag and drop electronic components onto the Read More
What is an Isolation Transformer?

An isolation transformer is made of two copper coils that are wound around each other and are each supplied by their own power source. While the term “isolation transformer” technically refers to any transformer, it is specifically a transformer that isolates a circuit from an alternating current. An isolation transformer does this by separating two circuits with an induction loop or decreasing the alternating current’s voltage before it reaches the circuit itself. How Isolation Transformers Work Isolation transformers work in the same way as other types of transformers. The isolation Read More
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying)
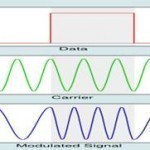
FSK (Frequency Shift Keying) is also known as frequency shift modulation and frequency shift signaling. Frequency Shift Keying is a data signal converted into a specific frequency or tone in order to transmit it over wire, cable, optical fiber or wireless media to a destination point. The history of FSK dates back to the early 1900s, when this technique was discovered and then used to work alongside teleprinters to transmit messages by radio (RTTY). But FSK, with some modifications, is still effective in many instances including the digital world where Read More
Charge-Coupled Device
A charge-coupled device (CCD) is a two-dimensional grid of semiconductor capacitors that can transfer charge between each other. While the term is widely used for image sensors, it actually describes the process by which the charges are transferred through the capacitors towards the grid edge. CCD History The concept of digital photography was first developed in 1961 at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, but it wasn't until 1969 that the first CCD was invented at Bell Labs. Commercial CCDs started appearing during the early 1970s, and one of the first uses Read More
Galvanic Isolator

A galvanic isolator is any device that connects two circuits together without allowing electricity to flow directly from one circuit to the other. Instead of transferring electricity through direct contact, galvanic isolators use other means, such as electromagnetism, mechanical devices, optical systems, or acoustic systems to convert the electricity into another form of energy, transfer it to an output device, and then convert it back into electricity. There are many different types of galvanic isolators and they can be used in a wide variety of applications. How Galvanic Isolators Work Read More
What Does DIN Stand For?
DIN stands for ‘Deutsches Institut für Normung’ which means ‘German Institute of Standardization’. DIN develops norms and standards as a service to industry, to the state and to society as a whole. It is a registered non profit organization which has been based in Berlin since 1917. It consists of nearly 1,700 members who include individual companies, associations, public authorities, and other organizations from industry, commerce, the trades and research. DIN members support standardization through membership fees and play an active part in the decision making process. DIN develops standards Read More
What is a Balun?

A balun is an electrical transformer that is used to convert electrical signals to and from balanced and unbalanced signals. They are normally used to connect lines that have different levels of impedance and are commonly used in the home for connecting HD and traditional antennas. Baluns are also used throughout industry, although it is not necessarily obvious when one is being used. What are the Types of Baluns? Autotransformer Balun – The autotransformer balun uses two coils that are placed tightly together on a ferrite rod. They are then Read More
Satellite Dishes
The major types of satellite dishes include motor-driven dishes, multi-satellites, VSAT, and ad hoc satellites. Other types include DTH, SMATV, CABD, automatic tracking satellite dishes, and big ugly dishes. A motor-driven satellite dish is mounted on a pole which rotates around an axis to detect and receive various satellite signals in the sky. It is driven by a stepper motor, which can also be controlled to face any satellite position in the sky. It’s standards, DiSEqC, USALs, and 36v positioners are supported by many receivers. DiSEqC stands for Digital Satellite Read More
Hall Effect
The Hall effect is the creation of a potential difference perpendicular to both the current flow in a conductor and the magnetic field which pass it. The Hall effect was discovered in 1879 by Edwin Hall, an American physicist. It has many applications such as measuring current and fluid flows. How the Hall Effect Works The charge carriers moving through the magnetic field are subjected to Lorentz force that deflect them away perpendicular to their normal path. This separation of charge carriers creates a potential difference between the opposite edges. Read More
Decibel Meter

A decibel meter (sound-level meter or loudness meter) is a device that measures and/or manipulates the loudness of an audio system or any other device that produces noise. Decibel meters are very common in industrial applications that require devices to produce a specific maximum noise, such as aircraft applications and audio devices. They are used in domestic applications in order to tune musical instruments, speakers, and power tools. Decibel meters can also be used in general outdoor applications to assess the loudness of background noise in a given area. How Read More


Share on: