Internet Authentication Service (IAS) is Microsoft's implementation of a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service) server and proxy. As a RADIUS server, IAS performs centralized connection authentication, authorization, and accounting for many types of network access, including wireless and VPN (Virtual Private Network) connections. As a RADIUS proxy, IAS forwards authentication and accounting messages to other RADIUS servers. The Authentication and Authorization Processes When a user tries to connect to a dial-up connection server or a Network Access Server (NAS)/Virtual Private Network (VPN) Server the following authentication requests are performed: Read More
Rootkit
A rootkit is a type of computer malware that is created to hide programs or other computer processes from detection from both users and antivirus software programs. Once installed, a rootkit will typically obtain administrator or higher-level permissions on the infected computer. Although rootkits originated with the UNIX operating system by providing root access to the software components installed with the malware (the kit portion of the name), they have since been developed to provide potentially rogue actors with access to computers running the Windows and Mac OS X operating Read More
How to Link a Charter Email with Outlook
A Charter Pipeline email account is a high speed Internet account obtained through www.charter.com. Since users can add several email accounts to their Outlook, they can send and receive email messages from their Charter Pipeline account through Outlook. How to Link a Charter Email with Outlook Open Outlook. Click the Tools menu and select E-mail Accounts… Select Add a new e-mail account and click Next. Choose POP3 as the server type by clicking the radio button and click Next. User Information Name: Enter the user’s name as it should appear Read More
Domain Kiting

Domain kiting (also known as ‘domain tasting’) refers to the method of exploiting loopholes in ICANN’s (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers) or other domain name registers’ (such as VeriSign) registration procedures in order to earn money from temporary domain registration or in order to test saleability or marketability of domain names. Registry companies have noted an increasing number of potentially fraudulent activities in recent years. For May 2007, over 35 million domain names were registered but only 2.7 million were permanent. The other names were ‘supposedly’ sent back Read More
Magnetic Air Car
A magnetic air car is a concept car that Magnetic Air Cars, Inc. designed and developed. The company is based in San Jose and currently holds the patent to the technology, albeit that it is understood that J.M. Custer from Piggott, Arkansas originally created the magnetic air car in 1932. The car ran on compressed air that an oscillating magnet generated. Although the car worked and did not run on fuel, the idea did not become popular due to cheap gasoline and the emergence of the much faster automobile. While Read More
Live CD

A live CD is a bootable CD-ROM disk that loads an operating system and has the ability to perform a specific set of tasks or functions. Live CD Minimum Requirements A system must have the following components to boot a live CD. Some items, such as a computer case, isn’t really necessary for a computer to function, but is expected to protect the computer components from the environment and other hazards that might damage them. All components should be assembled properly to create a working computer system. A Computer Case Read More
IPsec
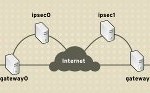
IPSec (IP Security) is a suite of protocols which was designed by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) to protect data by signing and encrypting data before it is transmitted over public networks. The IETF Request for Comments (RFCs) 2401-2409 defines the IPSec protocols with regard to security protocols, security associations and key management, and authentication and encryption algorithms. IPSec is a framework of open standards for encrypting TCP/IP traffic within networking environments. IPSec works by encrypting the information contained in IP datagrams through encapsulating. This in turn provides network level Read More
VoIP Security
Any technology that involves transfer of data or information is prone to compromised security. It happens with telephones, cell phones, email and Internet transactions. Because VoIP (Voice Over Internet Protocol) has the Internet as its mode of transference it’s possible to have your Internet-based called intercepted. To make matters worse, there are techno-troublemakers who are armed with the hacking skills needed to eavesdrop on virtually any call over the Internet they want to. It is impossible to ensure total security on information flow over the web including Internet based phone Read More
Data Dictionary
A data dictionary is an integral part of a database. It holds information about the database and the data that it stores, i.e., the meta-data. Any well designed database will surely include a data dictionary as it gives database administrators and other users easy access to the type of data that they should expect to see in every table, row, and column of the database, without actually accessing the database. Since a database is meant to be built and used by multiple users, making sure that everyone is aware of Read More
Transistor
The transistor is a solid-state component that uses a small current to control the flow of a large current. It is used mainly in amplification, detection, and switching. The transistor is one of the most important inventions of modern times. They are smaller, cheaper, and use less power than the vacuum tubes they replaced. Without transistors, the modern computer age would not be possible. History of the Transistor The transistor was invented in 1947 by three Americans at Bell Laboratories: John Bardeen, Walter Brattain, and William Shockley. They were trying Read More


Share on: